Overview
Hyperhidrosis (hi-pur-hi-DROE-sis) is excessive sweating that's not always related to heat or exercise. You may sweat so much that it soaks through your clothes or drips off your hands. Heavy sweating can disrupt your day and cause social anxiety and embarrassment.
Hyperhidrosis treatment usually helps. It often begins with antiperspirants. If these don't help, you may need to try different medications and therapies. In severe cases, your health care provider may suggest surgery to remove the sweat glands or to disconnect the nerves related to producing too much sweat.
Sometimes an underlying condition may be found and treated.
Products & Services
Symptoms
The main symptom of hyperhidrosis is heavy sweating. This goes beyond the sweating from being in a hot environment, exercising, or feeling anxious or stressed. The type of hyperhidrosis that usually affects the hands, feet, underarms or face causes at least one episode a week when you're awake. And the sweating usually happens on both sides of the body.
When to see a doctor
Sometimes excessive sweating is a sign of a serious condition.
Seek immediate medical attention if you have heavy sweating with dizziness, pain in the chest, throat, jaw, arms, shoulders or throat, or cold skin and a rapid pulse.
See your health care provider if:
- Sweating disrupts your daily routine
- Sweating causes emotional distress or social withdrawal
- You suddenly begin to sweat more than usual
- You experience night sweats for no apparent reason
Causes
Sweat glands
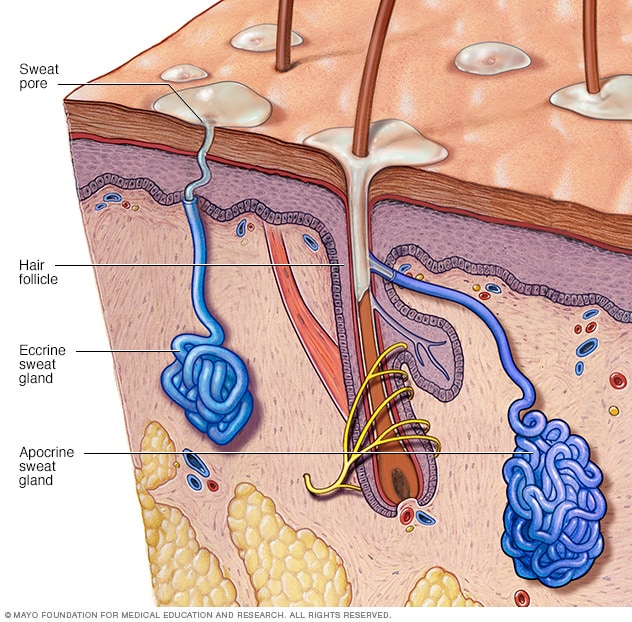
Sweat glands
Eccrine sweat glands occur over most of the body and open directly onto the skin's surface. Apocrine glands open into the hair follicle, leading to the surface of the skin. Apocrine glands develop in areas with many hair follicles, such as on the scalp, armpits and groin. Eccrine sweat glands are involved in hyperhidrosis, though apocrine glands may play a role as well.
Sweating is the body's mechanism to cool itself. The nervous system automatically triggers sweat glands when your body temperature rises. Sweating also occurs, especially on your palms, when you're nervous.
Primary hyperhidrosis is caused by faulty nerve signals that trigger eccrine sweat glands to become overactive. It usually affects the palms, soles, underarms and sometimes the face.
There is no medical cause for this type of hyperhidrosis. It can run in families.
Secondary hyperhidrosis is caused by an underlying medical condition or by taking certain medications, such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and some diabetes and hormonal medications. This type of hyperhidrosis may cause sweating all over the body. Conditions that might cause it include:
- Diabetes
- Menopause hot flashes
- Thyroid problems
- Some types of cancer
- Nervous system disorders
- Infections
Risk factors
Risk factors for hyperhidrosis include:
- Having a blood relative, such as a parent, sibling or grandparent, who sweats heavily
- Taking medicines or supplements that cause sweating
- Having a medical condition that causes sweating
Complications
Complications of hyperhidrosis include:
- Infections. People who sweat a lot are more prone to skin infections.
- Social and emotional effects. Having clammy or dripping hands and sweat-soaked clothes can be embarrassing. Your condition may affect your pursuit of work and educational goals.
Oct. 25, 2024